
In today’s digital world, computers are learning to ‘see’ and ‘understand’ images just like humans. But how do they do it? This fascinating journey involves two key fields: Computer Vision and Image Processing. While they may sound similar, they have distinct roles in the world of technology. Let’s dive in to understand these exciting fields better!
What is Image Processing?
The Art of Beautifying Images
Imagine you have a photograph that isn’t quite perfect – maybe it’s too dark, or the colors are dull. Image processing is like a magic wand that transforms this photo into a better version. It involves altering or improving digital images using various methods and tools. Think of it as editing a photo to make it look more appealing or to highlight certain features. It’s all about changing the image itself.
What is Computer Vision?
Teaching Computers to Interpret Images
Now, imagine a robot looking at the same photograph. Unlike humans, it doesn’t naturally understand what it’s seeing. This is where computer vision comes in. It’s like teaching the robot to recognize and understand the content of the image – is it a picture of a cat, a car, or a tree? Computer vision doesn’t change the image. Instead, it tries to make sense of it, much like how our brain interprets what our eyes see.
Core Principles & Techniques
Computer Vision (CV): Seeing Beyond the Surface
In the realm of Computer Vision, the goal is to teach computers to understand and interpret visual information from the world around them. Let’s explore some of the key principles and techniques that make this possible:
Pattern Recognition
Think of this as teaching a computer to play a game of ‘spot the difference’. By recognizing patterns, computers can identify similarities and differences in images. This skill is crucial for tasks like facial recognition or identifying objects in a scene.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is like giving a computer a very complex brain that learns from examples. By feeding it thousands, or even millions, of images, a computer learns to identify and understand various elements in these images. This is the backbone of modern computer vision, enabling machines to recognize objects, people, and even emotions.
Object Detection
This is where computers get really smart. Object detection is about identifying specific objects within an image. It’s like teaching a computer to not just see a scene, but to understand what each part of that scene is. For instance, in a street scene, it can distinguish cars, people, trees, and buildings.
Image Processing: Transforming Pixels into Perfection
In the world of Image Processing, the magic lies in altering and enhancing images to make them more useful or visually appealing. Let’s break down some of the fundamental principles and techniques:
Image Enhancement
This is like giving a makeover to an image. Image enhancement can brighten up a dark photo, bring out hidden details, or make colors pop. It’s all about improving the look and feel of an image to make it more pleasing or informative.
Filtering
Imagine sifting through the ‘noise’ to find the real picture. Image filtering involves removing or reducing unwanted elements from an image, like blurring, smoothening rough edges, or sharpening blurry parts. It helps in cleaning up the image to highlight the important features.
Transformation Techniques
This is where an image can take on a new shape or form. Transformation techniques might include resizing an image, rotating it, or even warping it to change perspective. It’s like reshaping the image to fit a specific purpose or requirement.
These techniques form the toolbox of image processing, enabling us to manipulate and enhance images in countless ways.
Distinctions Between Computer Vision and Image Processing
Image Processing: Visual Perfection
The primary aim of image processing is to improve image quality. Whether it’s enhancing contrast, adjusting colors, or smoothing edges, the focus is on making the image more visually appealing or suitable for further use. It’s about transforming the raw image into a refined version of itself.
Image processing focuses on enhancing and transforming images. It’s vital in fields like digital photography for color correction, medical imaging for clearer scans, and graphic design for creating stunning visuals. These transformations not only improve aesthetics but also make images more suitable for analysis, laying the groundwork for deeper interpretation, including by computer vision systems.
Computer Vision: Decoding the Visual World
Computer vision, on the other hand, seeks to extract meaning from images. The goal isn’t to change how the image looks but to understand what the image represents. This involves identifying objects, interpreting scenes, and even recognizing patterns and behaviors within the image. It’s more about comprehension rather than alteration.
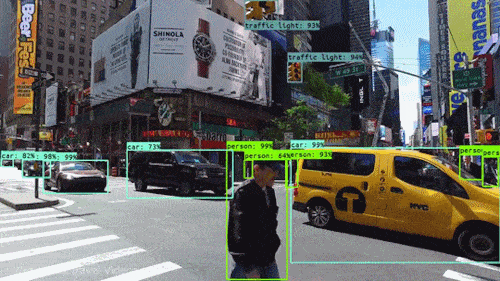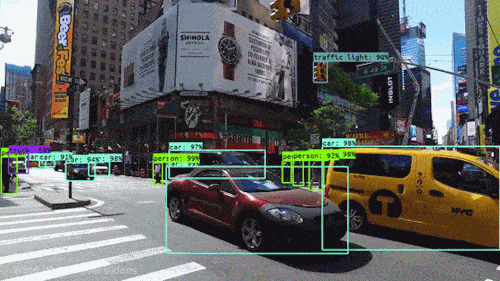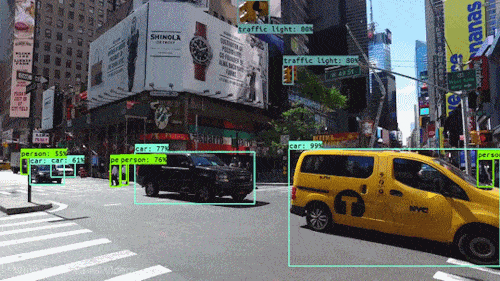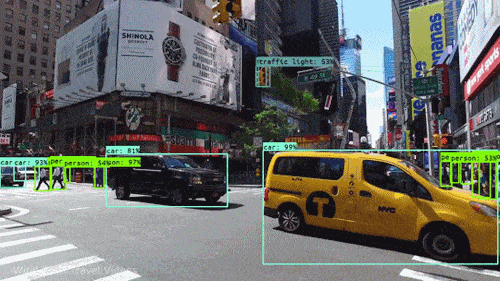
Computer Vision, conversely, aims to extract meaning and understanding from images. It’s at the heart of AI and robotics, helping machines recognize faces, interpret road scenes for autonomous vehicles, and understand human behavior. The success of these tasks often relies on the quality of image processing. High-quality, well-processed images can significantly enhance the accuracy of computer vision algorithms.
Techniques and Tools
Image Processing Techniques and Tools
In image processing, the toolkit includes a range of software and algorithms specifically designed for modifying images. This includes:
Software like Photoshop and GIMP, for manual edits such as retouching and resizing.
Algorithms for automated tasks like histogram equalization for contrast adjustment and filters for noise reduction and edge enhancement.
Computer Vision Techniques and Tools
Computer Vision, on the other hand, employs a different set of methodologies:
Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are pivotal for tasks like image classification and object recognition.
Pattern Recognition Tools are used to identify and classify objects within an image, essential for applications like facial recognition.
Interconnection and Overlap: Synergy in Sight
This section illustrates the essential relationship between image processing and computer vision, showcasing their collaborative role in advanced technological applications.
Building Blocks: Image Processing in Computer Vision
Image Processing often serves as the foundation for Computer Vision tasks. For instance:
Pre-processing in Computer Vision: Many computer vision algorithms require pre-processed images. Techniques like noise reduction and contrast enhancement from image processing improve the accuracy of computer vision tasks.
Feature Extraction: Simplified or enhanced images from image processing are easier for computer vision algorithms to analyze and interpret.
Integrated Systems: Collaborative Power
Both fields often work in tandem in complex systems:
Autonomous Vehicles: Computer vision systems rely on image processing to clarify and enhance road imagery for better object detection and obstacle avoidance.
Medical Imaging Analysis: Image processing is used to enhance medical images like MRIs or X-rays, which are then analyzed by computer vision algorithms for diagnosis and research.
Applications and Real-World Examples: Transforming Industries
Diverse Industries Benefiting from These Technologies
Healthcare
Medical Imaging: Image processing enhances medical scans for clarity, which are then analyzed by computer vision to detect abnormalities, aiding in early diagnosis and treatment planning.
Automotive
Autonomous Vehicles: Utilize image processing for clear visual input, which is essential for computer vision systems to accurately identify and react to road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
Surveillance
Security Systems: Image processing improves image quality from cameras, aiding computer vision in accurately recognizing faces or suspicious activities and enhancing security measures.
Entertainment
Film and Gaming: Image processing is used for visual effects, while computer vision contributes to interactive experiences, like augmented reality games.
Case Studies: Integrating Computer Vision and Image Processing
Smart City Projects
Traffic Management Systems: Utilize image processing to enhance traffic camera feeds, which are then analyzed by computer vision for managing traffic flow and detecting incidents.

Agricultural Technology
Crop Monitoring Systems: Image processing clarifies aerial images of crops, and computer vision analyzes these images to assess crop health and growth, optimizing agricultural practices.
These examples and case studies highlight the impactful and transformative role of image processing and computer vision across various sectors, demonstrating their critical contribution to technological advancements.
Conclusion: The Convergence of Vision and Processing in the Digital Age
summary, Computer Vision and Image Processing, though distinct in their goals and techniques, are interconnected fields that play a pivotal role in the advancement of modern technology. Image processing sets the stage by enhancing and transforming images, which are then interpreted and understood through computer vision. Together, they are revolutionizing industries such as healthcare, automotive, surveillance, and entertainment, driving innovation and opening new frontiers in technology.
Understanding these fields and their interplay is crucial for anyone looking to engage with the latest in tech development and application.









5K+ Learners
Join Free VLM Bootcamp3 Hours of Learning