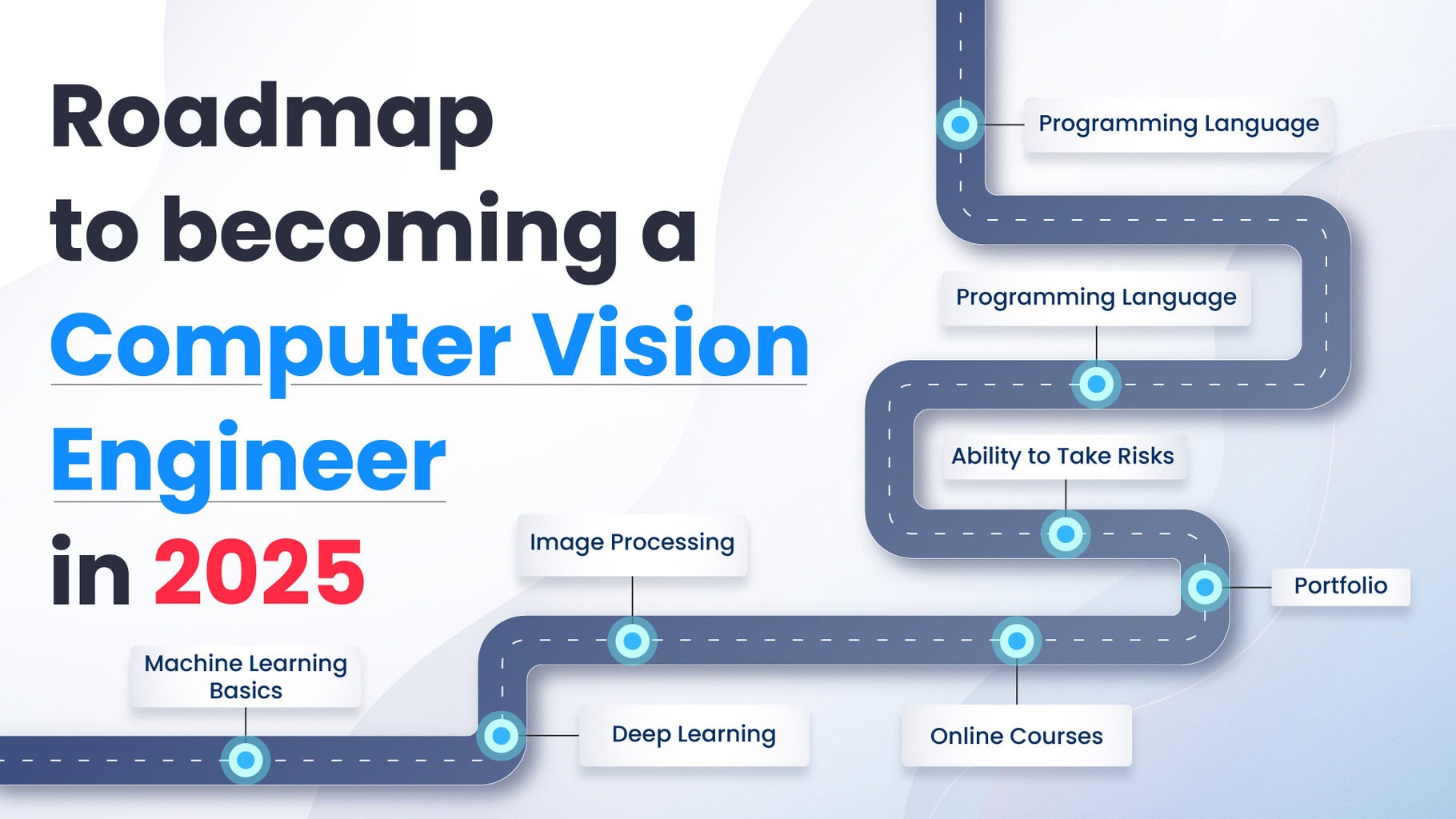
Introduction
In this digital day and age, where technological advancements are at an unprecedented pace, one field that stands out is Computer Vision. This read is for aspiring individuals who wish to navigate the computer vision landscape. From mastering the fundamentals of image processing to exploring the many deep learning concepts, we delve into the essential skills, industries, market trends, and much much more.
Table of Content
Introduction
What is Computer Vision
Who is a Computer Vision Engineer
Skills needed to become a Computer Vision Engineer
Stages of growth for a Computer Vision Engineer
Where does a Computer Vision Engineer Work
Income of a Computer Vision Engineer
Computer Vision Market Trends
Conclusion
What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision, or Machine Vision, is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence that facilitates machines and computer systems to derive valuable information from digital images, videos, and other visual data.
To learn more, check out our Beginner’s Guide article as we delve into the nitty gritty of Computer Vision.
Who is a Computer Vision Engineer?
A Computer Vision Engineer is one who tries to recreate a human visual system into machines leveraging various machine vision tools and algorithms. They analyze and handle large amounts of data in the form of datasets to assist in automating predictive decision-making through visuals. Simply put, a Computer Vision Engineer is one who works with visual information derived from images and videos.
Most Vision engineers spend their time researching, training, testing, and deploying models that are implemented in computer vision applications to solve real-world problems. They also work closely with other engineers to build hardware and software leveraging visual information to solve problems or perform specific tasks. They possess impressive knowledge in topics such as machine learning, deep learning, image annotation, image and video segmentation, and image recognition, to name a few. They are high in demand across various industries like healthcare, automotive, robotics, and surveillance.
Being a CV Engineer is not a walk in the park; it requires a lot of dedication and effort for research and study due to the sheer vastness of the subject. But do not fret! This beginner’s guide will walk you through the steps to becoming a Pro Computer Vision Engineer. So let’s get to it!
Skills Needed to Become a Computer Vision Engineer
Mathematics
Your journey to becoming a Computer Vision expert starts with Mathematics. It is imperative for one to conquer Math. It is used for the representation and manipulation of images. A CV pro would have a very good understanding of the relation between images and their numerical representations. Let us explore a few Mathematical concepts you need to master.
Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra is one of the foundational aspects of Computer Vision to master. Let us look at a few instances of its usage.
At a basic level, images are represented as matrices or multi-dimensional array of numbers. Linear Algebra manipulates these matrices that are essential for various image-processing tasks.
Another CV task is the detection and description of certain features within an image, like edges, corners, or specific objects. Algorithms used to perform these operations, such as HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients), leverage Linear Algebra for more efficient computation.
Operations like rotation, scaling, and translation are fundamental in CV. These are expressed using matrices and vectors, which form a part of the core concepts of Linear Algebra.

In the realm of image processing, convolution operations are used for filtering and image transformations. Implementing these convolutions in the context of deep learning is made possible with Linear Algebra.
Another important aspect of computer vision is 3D vision and depth perception. Gaining insights from 3D scenes and depth from 2D images like camera calibration, stereo vision, and structure from motion involves calculations based on Linear Algebra.
Linear Algebra provides mathematical frameworks and tools essential for various Computer Vision tasks.
Calculus
Calculus, particularly differential calculus, is crucial in Computer Vision.
Let us take the case of Deep Learning. Understanding DL models forms a significant part of Computer Vision, and once again, Calculus concepts are used widely. For instance, the backpropagation algorithm for training neural networks is based on calculus.
Feature extraction is another Computer Vision task. It involves extracting meaningful features from images which is also made possible by Calculus. Take the instance of SIFT or Scale-invarient feature transform and edge detection. Facilitated by Calculus, they are able to identify key points and features in an image that are essential for tasks like image matching and object recognition.
Motion analysis and tracking also use Calculus. How so? Derivatives are calculated in space and time to understand how objects move in a scene.
Understanding the principles of Calculus is key to understanding CV algorithms and techniques.
Probability and Statistics
CV deals with a lot of uncertainties and variability in data. This is where Probability and Statistics come in. Let us look at a few of them.
Optimizations of Deep Learning models are made possible with Statistical techniques. Methods like stochastic gradient descent rely on probabilistic approaches to find optimal parameters for neural networks.
Statistical methods are used to detect and track objects in a sequence of images or video. The movement of objects is predicted using probabilistic models.
Machine Learning models that form a big chunk of Computer Vision also use Probability and Statistics. Models such as CNNs or Convolutional Neural Networks use statistical data to recognize and classify patterns in images.
Programming
Programming forms another important part of Computer Vision. Let us see why.
Before any images or videos can be analyzed, they need preprocessing. This is where programming comes into the picture. They are used to perform tasks like normalizing data, image resizing, and noise filtration.
At the core of Computer Vision, we have algorithms. Tasks such as object detection, image classification, or pattern recognition are implemented with algorithms. And you guessed it right, programming is used to create these algorithms.
With most applications, CV algorithms are required to operate in real time. Once again, Programming comes to the rescue by optimizing the algorithms for speed and efficiency, ensuring live video feeds can be processed quickly.

Many CV tasks leverage ML and DL techniques. With programming, the performance of these models are optimized and integrated into larger systems. This involves working with neural networks, setting up training pipelines, and using Vision libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
In an academic or research environment that involves exploring new computer vision techniques, programming is used to conduct experiments and validate hypotheses.
The next question arises, which language do I start with? Let us explore a few of them.
Python
Python is one of the most popular programming languages for Computer Vision mainly due to its simplicity and a vast array of libraries like OpenCV, TensorFlow, and PyTorch for image processing and machine learning. Due to its versatility and ease of integration, Python is widely used for academic research.
If you’re confused about where to start your Python journey, we’ve got you covered with a comprehensive yet concise Free Python Bootcamp designed specifically for beginners. Whether you’re aiming for AI, data science, or automation, this bootcamp is the perfect launchpad.
C++
C++ is a powerful programming language used in scenarios where memory management, real-time processing, and execution speed are crucial. Core algorithms in libraries such as OpenCV were originally written in C++. It also supports most of the libraries. C++ is widely used in real-time image processing, resource optimization tasks, embedded systems, and robotics, where computer vision has a role.
MATLAB
MATLAB is a high-level language developed by MathWorks that has extensive use in computer vision.
It has robust tools for data visualization that are essential for image and video analysis. It also is used for creating user interfaces for ease of use and interaction with computer vision applications.
MATLAB allows for integration with other languages offering more flexibility and leveraging other libraries and tools.
MATLAB assists in integrating computer vision algorithms into larger systems with Simulink, allowing for model-based design and a graphical programming approach. This is particularly used in embedded systems and control design.
Novices usually start with Python due to its simplicity and then proceed to master other languages. Programming forms one of the foundational parts of your journey to Computer Vision mastery.
Machine Learning Concepts
Machine learning has a crucial role in computer vision. It significantly enhances CV capabilities and applications. Let us explore some of the key roles of machine learning in computer vision.
Pattern recognition is very crucial in visual data. This is important for tasks like object recognition, where the system identifies and classifies objects within images or videos. This is made possible with machine learning algorithms.
Another key aspect of understanding the context of visual data is feature detection and extraction. It includes identifying key points, edges, and shapes in images. Once again, ML comes to the rescue by detecting and extracting features.
Machine learning algorithms can analyze and interpret images and videos to detect anomalies, track movements, and even predict future occurrences based on visual cues.
Then there is semantic segmentation, which is the process where each pixel in an image is classified into a category, helping in understanding the scene at a more detailed level. Machine learning makes this possible.
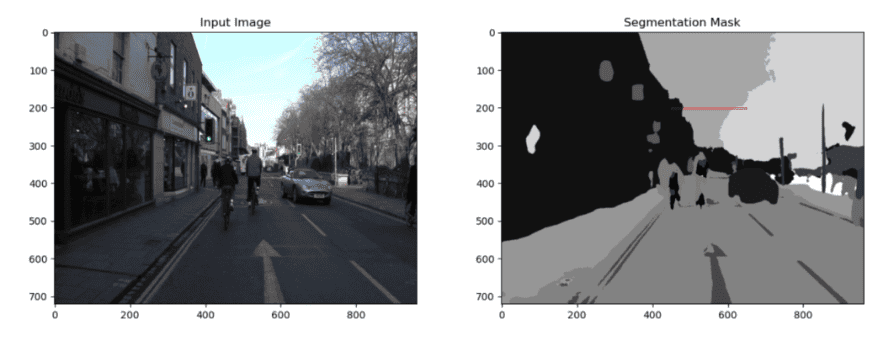
Machine learning algorithms can also track objects in motion across frames in a video, which is crucial in surveillance, sports analysis, and autonomous vehicles.
Machine learning enhances AR and VR experiences by enabling real-time image processing and interaction with the environment.
This concept allows a model developed for a task to be reused as the starting point for a model on a second task, facilitating faster and more efficient training of computer vision models.
Machine learning concepts have had a big impact on computer vision, enabling advanced image processing, real-time analysis, and the ability to extract and utilize complex patterns from visual data.
Computer Vision Theory
The next step is building a solid foundation in Computer Vision Theory. Let us look at some of the key theories.
Convolutional Neural Networks
CNN is a critical theory in computer vision. They are designed to learn spatial hierarchies of features from input images. They form a huge part of tasks such as image recognition, classification, and segmentation.
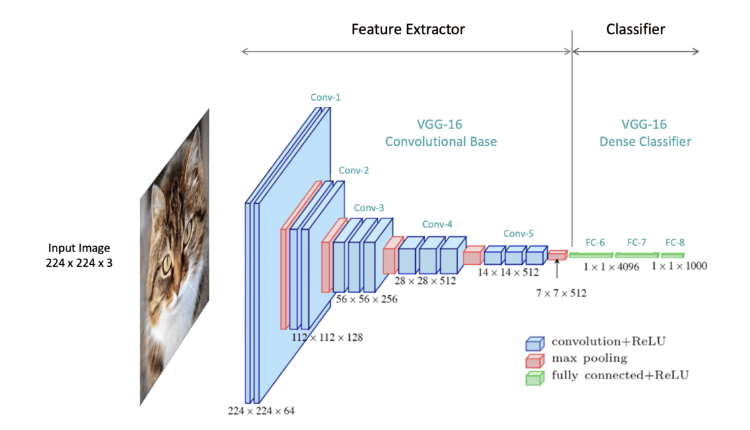
Image Processing
Another fundamental concept of computer vision is Image Processing. It involves techniques to enhance raw images received from cameras and sensors. This can include noise reduction, contrast enhancement, and image sharpening, which are crucial for improving the accuracy of further processing.
Pattern Recognition
As the name suggests, it involves recognizing patterns and regularities in data. This includes identifying specific objects, faces, or scenes in images in CV. Techniques like template matching, feature-based matching, and statistical classification fall under this section.
Computer Graphics
Geometric aspects of an image, like perspective, shape, and motion, are key. Theories related to 3D reconstruction, camera calibration, and stereo vision are extensively used to interpret spatial relationships in images.
Deep Learning
Beyond the spatial hierarchies of Convolutional Neural Networks, we have Deep Learning that includes various architectures like autoencoders, GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), and RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks) that are used for complex tasks like image generation, style transfer, and video analysis.
Feature Extraction
With Feature Extraction, it identifies key points or features in images like edges and corners and finds correspondences between different images. This is crucial for tasks like object recognition, motion tracking, and panorama stitching.
Semantic Segmentation
This theory focuses on image analysis at the pixel level, aimed at classifying every pixel into a specific category. Semantic Segmentation finds use in scene understanding, autonomous driving applications, and medical imaging applications.
All these theories are crucial and come into play when addressing different aspects and challenges in visual data interpretation and understanding. They facilitate the proper functioning of a wide range of tasks, from simple image classification to complex scene understanding and interaction with the physical world.
Image Processing Techniques
Image Processing is the method of manipulating images into a digital form to perform specific operations to infer some useful information from it. It is done for the enhancement of an existing image to get the relevant information from it. Image processing is an essential preprocessing step in many applications like object detection and face recognition. For instance, in the entertainment industry, image manipulation is used to add or remove objects to images. Let us explore them.
Image Enhancement
Image enhancement in image processing for computer vision refers to a set of techniques used to improve the visual appearance of an image or to convert the image to a be better suited for analysis by humans or computer algorithms. This process is crucial in preparing images for further tasks in computer vision, such as feature extraction, object detection, and classification. The goal is often to increase the quality of the original image from the perspective of an observer or to enhance certain image features important for further processing. Why is Image enhancement crucial? Let us see why.
- Image enhancement aids in contrast adjustments. With techniques like histogram equalization or contrast stretching, pixel intensity is modified for clearer images.
- The image brightness is enhanced by adjusting pixel values, either simply or through complex methods.
- Image smoothening is performed by minimizing random brightness or color variations using methods like Gaussian blurring, median, or bilateral filtering.
- It also performs edge enhancements by making image edges more distinct and leveraging techniques like unsharp masking, laplacian filters, and high-pass filters.
- Color Balance and Saturation: Improving visual appeal or emphasis by correcting color temperature and enhancing color vividness.
- Deblurring: Restoring sharpness to blurred images caused by motion or focus issues.
- Geometric Processing: Manipulating image structures for noise removal, object separation, or shape emphasis.
Image Restoration
Image restoration is the process of enhancing the quality of an image by removing noise. Although there are a few similarities with image enhancement, the latter leverages the characteristics of the human visual system for better-looking results. In image restoration, the original image quality is high but in certain conditions. Here are a few aspects of image restoration.
- One of the key aspects of image restoration is removing noise from images like Gaussian noise or speckle noise.
- Another aspect is improving the resolution of an image. This could be enlarging lower-resolution images by increasing the number of pixels in an image.
- Blurring of images is another common problem. This could be due to out-of-focus captures or other factors. This is tackled by estimating the blur patterns or blur kernel and reversing its effects.
- Color correction is another important aspect of image restoration. For instance, some images will have color distortions, or older images will have faded colors. Such images will need color correction by adjusting the color balance of images.
Inpainting to do Image Restoration
Image Compression
Image compression is the process of applying data compression on digital images. The intent behind this is to optimize the size of the image data to make it more storable and transmittable. It can be broadly classified into
Lossless compression
This process refers to making smaller versions of an image without compromising the quality of the image. It is a reversible process, and the image parts are still intact.
Lossy compression
In this process, the image size is reduced by removing some parts of the image. We will get a significantly smaller version of the image, making it much faster to load with minimal quality difference. One of the downsides is unlike the lossless compression, this is not reversible.
Image Manipulation
Image manipulation is the process of modifying digital images. This step is done to improve image quality or create visual effects. Here are a few uses of image manipulation
Image processing assists with filtering. It is a commonly used technique for blurring, sharpening, or edge detection that forms a fundamental part of image processing.
Another aspect is composite image creation which involves combining different images to create a new image commonly used in advertising.
Not only putting images together but also dividing them into different parts is performed with image manipulation. This is done based on the characteristics of the pixels in an image.
We can also perform operations such as dilation, opening and closing, and erosion which find use in image pre-processing, especially with binary images through Morphological processing.
Deep Learning Models and Methods
Let us bring our focus to another important key to Computer Vision proficiency – Deep Learning.
Mastering various deep learning models and methods is crucial for a computer vision engineer. Proficiency in models like CNNs, GANs, and Vision Transformers helps one solve problems ranging from image recognition to real-time object detection.
- Let’s kick things off with CNNs. Also known as Convolutional Neural Networks, they form the building blocks of analyzing an image. Their architecture mimics human visual systems offering more effective feature extraction and pattern learning. They excel in tasks like image recognition and image classification and find use in autonomous driving and facial recognition applications.
- Now we move to RNNs. Recurrent Neural Networks. They decipher temporal relationships and sequential context within visual data, which are useful for applications like frame prediction or video captioning. They are good at understanding sequential data like action recognition or video analysis.
- RNNs and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) are very good at handling time series data and sequences, offering more coherent interpretations in vision tasks.
- Then we have Autoencoders. They are primarily used for unsupervised learning like feature learning and image dimensionality reduction. They play a key in tasks like noise reduction and image reconstruction and find use in applications like image denoising and anomaly detection.
- Coming to GANs, or Generative Adversarial Networks, are powerful models enabling generating new images and augmenting datasets. They help create realistic synthetic images and enhance datasets for training other models generating high-res images. They have the incredible ability to mimic complex data distributions. Some applications include
- Generating realistic textures and objects for more immersive AR experiences
- Generate varied, realistic training data for facial recognition and biometric authentication
Understanding these models makes one more efficient problem-solver and can make optimizations of computational resources, thereby upscaling their knowledge to the road to success.
Stages of growth for a Computer Vision Engineer
Embarking on a career as a computer vision engineer is an exciting one. The pathway of a Computer Vision expert can be broken down into several key stages, each adding its own challenges and rewards. Let us explore them.
Junior Computer Vision Engineer
Most CV engineers’ careers start here. As a junior engineer, you’ll have to learn and absorb as much as possible. You’ll work on small modules of larger projects, getting your hands on image processing algorithms, machine learning models, and data annotation tasks. This is the stage for honing technical skills and understanding the practical applications of theoretical knowledge.
Computer Vision Engineer
With a few years of experience, you move into a more independent role. Here, you would design and implement parts of computer vision systems, troubleshoot problems, and optimize performance. At this stage, you’ll dive deeper into advanced algorithms and explore areas like object detection, facial recognition, or 3D reconstruction. You will start contributing solutions to different projects and applications.
Senior Computer Vision Engineer
Now we’re slowly moving into the serious stuff. As a senior engineer, you would take on complex challenges and also lead segments of projects. This stage includes refining and developing sophisticated algorithms in areas like deep learning and neural networks, which could involve experimenting with new forms of image and video analysis and accuracy enhancements in object detection and recognition. At this stage, you’re not just solving problems but also identifying them. You’ll also mentor junior team members, sharing your expertise and experience.
Project Manager
At this stage, you oversee entire projects. This role demands a fine balance between technical knowledge and managerial skills. You transition from hands-on technical work to managing computer vision projects. Your duties encompass project planning and ensuring timelines and resources are well-managed. Leadership is key; you mentor and guide a team of engineers, fostering a collaborative environment. Stakeholder communication becomes crucial, as you’re the bridge between your team and external parties. Your impact is measured by the success of your projects, the growth of your team, and the value delivered to stakeholders.
Solutions Architect
As a Solutions Architect, you bridge the gap between technical aspects and practical applications. As a solutions architect, your role becomes more consultative. You design and architect complex computer vision systems, often interfacing with clients or other departments to understand their needs and translate them into technical requirements. Your expertise helps make crucial decisions about the right tools, technologies, and approaches for each project.
Principal Computer Vision Engineer
At the pinnacle of this career path is the Principal Computer Vision Engineer. This role focuses on technological advancements and research, exploring new territories of AI and machine learning. Some key aspects of this role involve networking with other thought leaders, contributing to academic journals, and speaking at conferences. Ideally, at this stage, your work has the potential to influence the broader landscape of the industry, setting new standards and opening up possibilities.
Like any other career path, the path of a computer vision engineer involves continuous learning and skill development. Every step offers valuable experiences that bring about both personal and field-wide advancements.
Although the computer vision path seems daunting at first, it proves to be immensely rewarding in the long run.
Where does a Computer Vision Engineer work?
In today’s fast-paced digital era, the role of Computer Vision Engineers is becoming increasingly crucial. Companies ranging from startups to MNCs leverage computer vision to automate processes, make more informed decisions, and create seamless customer experiences.
However, finding such skilled individuals is a challenge. The scarcity of talent has led to a high demand for vision engineers. Companies recognize these professionals’ value and are willing to pay premium salaries to secure the best in the market. The high salaries commanded by Computer Vision Engineers are a testament to their indispensable role in modern businesses.
Let’s explore some of the industries.
Tech Companies
Large tech companies, especially those at the cutting edge of artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and autonomous systems, are prime employers for computer vision engineers. MegVii, Nauto, SenseTime, and Tractable are a few of the Computer Vision tech giants. Engineers collaborate closely with fellow tech professionals in these office-based roles, contributing to developing groundbreaking technologies.
Research Institutions
Both academic and private research institutions are very good for advancing your computer vision’s theoretical and practical aspects. In such environments, you engage in research that pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in this exciting field.
Startups
Startups, particularly in AI, robotics, and software development, are hotspots for computer vision talent. Companies such as Matterport, Hive, Mitek Systems and MetMap are few of the leading startups in the United States. These environments are known for their dynamism and fast pace, allowing engineers to work on innovative and transformative projects.
Automotive Industry
Self-driving cars are the talk of the decade with brands like Tesla and Google’s Waymo. The development of self-driving cars and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) heavily relies on the expertise of computer vision engineers. These professionals are essential in steering the future of autonomous vehicles.
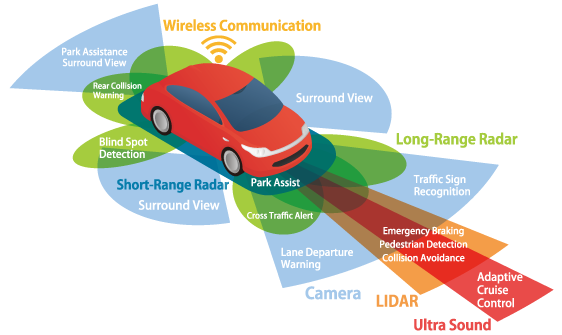
Healthcare
The healthcare sector is another industry that benefits immensely from the skills of computer vision engineers. From medical imaging to diagnostics and treatment planning, these engineers play a crucial role in advancing medical technology. AiCure, Tempo, Moon Surgical, and Ibex are some healthcare brands leveraging Computer Vision.
Manufacturing
Today’s manufacturing scene is nothing without automation. Manufacturing brands leverage industrial automation with computer vision engineers who work to improve processes through automation. Tasks such as quality control, safety monitoring, and operational efficiency are key in modern manufacturing environments.
Retail
Coming to the world of retail and commerce, computer vision tech is used for inventory management, analyzing customer behavior, and enhancing overall shopping experiences. Engineers work on the integration of advanced vision capabilities into the commercial space.
Security and Surveillance
Projects related to surveillance, national security, and defense technology often require the specialized skills of computer vision engineers. Their work in this sector is critical and often involves top-level security and technological innovation.
As we can see, the opportunities are vast across various industries and rely on the individual’s personal interests and career aspirations.
Income of a Computer Vision Engineer
In this section, we’ll take a closer look at what computer vision engineers can expect to earn in India, the USA, and Europe, specifically Germany.
In India, the average annual salary for a computer vision engineer stands at ₹7,47,370. However, this is just the base. There’s often additional cash compensation, which averages around ₹97,370. These figures are derived from 171 salary submissions by computer vision engineers to Glassdoor, providing a transparent view of what one can expect to earn in this field in India.
Moving to the United States, the salary landscape for computer vision engineers is quite competitive and lucrative. On average, they earn about $165,156 annually, which breaks down to approximately $79.40 per hour. The entry-level positions offer around $136,200 annually for those just starting in the field. At the higher end, experienced computer vision engineers can make up to $204,000 annually, showcasing the high demand and value of experience in this sector.
In Germany, the average gross salary for a computer vision engineer is about 93,064 Euros per year, equating to around 45 Euros per hour. Additionally, these engineers often receive an average bonus of 4,020 Euros. Salary scales vary with experience; entry-level engineers with 1-3 years of experience earn around 65,231 Euros annually. In contrast, those with over 8 years of experience can expect an average salary of about 115,599 Euros, indicating a significant growth potential in earnings with experience and expertise.
These salary figures give a clear view of what computer vision engineers can expect in terms of remuneration in these diverse markets. It’s evident that as one gains experience in this field, the financial rewards can be quite substantial.
Computer Vision Market Trends
The computer vision market is growing fast. In 2022, it was worth $14.10 billion, and it’s expected to grow even more, at a rate of 19.6% each year, from 2023 to 2030. This growth is mainly because Artificial Intelligence (AI) is used in things like drones and self-driving cars.
- New tech in cameras and learning systems has made computer vision useful in many areas like schools, hospitals, robots, electronics, shops, factories, and security. For example, in 2022, TachyHealth and Medical Refill worked together to use computer vision to help doctors understand medical tests better and make treatment more interactive for patients.
- Security is one area where computer vision is really useful. It scans faces and fingerprints to protect important places and things. For instance, your phone might use face recognition for security. Another example is the collaboration between IDEMIA and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security in 2022 to use facial recognition for public safety.
- Self-driving cars are a big deal in the computer vision market. These cars use cameras and sensors to see road signs and avoid obstacles. In 2021, Aventior talked about how computer vision makes self-driving cars safer by helping them see better and understand their surroundings.
- Manufacturing is also using more computer vision as factories become more automated. The Internet of Things (IoT) is making factories smarter, and computer vision is helping to keep an eye on how things are made. Amazon Web Services started a service called “Amazon Lookout” in 2021 to make it easier for factories to use computer vision to check their products.
Computer vision is changing many industries by making things smarter and safer.
If you’re curious about how computer vision works and want to build real-world projects using images and video, our OpenCV Bootcamp is the perfect place to start.
Conclusion
And that’s a wrap of this A to Z comprehensive guide to becoming a Computer Vision Engineer in 2025. We journeyed through the evolving path of computer vision engineering. We discussed the skills you need to acquire, like deep learning image processing, which can open up a ton of opportunities across diverse industries. Whether it’s revolutionizing healthcare, transforming automotive safety, or reinventing retail experiences, your role as a computer vision engineer is front and center. We also delved into the pay grade and discussed the current market trends, indicating a steady climb.
2025 is the year to chase your vision (no pun intended) to become a Pro Computer Vision Engineer. See you guys in the next one!
If you’re committed to making significant progress in your AI career, the CVDL Master Program is designed to provide you with a structured, comprehensive learning path—from foundational concepts to advanced AI applications. With real-world projects, industry-ready skills, and hands-on experience, it’s time to invest in yourself and join a community of learners striving for success.
Enroll in the CVDL Master Program Today and start transforming your career!










5K+ Learners
Join Free VLM Bootcamp3 Hours of Learning